Cyber Warfare
1. What is Cyber Warfare
Cyber warfare is usually defined as a cyber attack or series of attacks that target a country. It has the potential to throw the government and civilian infrastructure into chaos and disrupt critical systems, resulting in damage to the state and even loss of life.
There is, however, a debate among cyber security experts as to what kind of activity constitutes cyber warfare. The US Department of Defense recognizes the threat to national security posed by the malicious use of the Internet but doesn’t provide a clearer definition of cyber warfare. Some consider cyber warfare to be a cyber attack that can result in death.
Cyber warfare typically involves a nation-state perpetrating cyber attacks on another, but in some cases, the attacks are carried out by terrorist organizations or non-state actors seeking to further the goal of a hostile nation. There are several examples of alleged cyber warfare in recent history, but there is no universal, formal, definition for how a cyber attack may constitute an act of war.


2. 7 Types of Cyber Warfare Attacks
-
Espionage
Refers to monitoring other countries to steal secrets. In cyber warfare, this can involve using botnets or spear phishing attacks to compromise sensitive computer systems before exfiltrating sensitive information.
· Sabotage
Government organizations must determine sensitive information and the risks if it is compromised. Hostile governments or terrorists may steal information, destroy it, or leverage insider threats such as dissatisfied or careless employees, or government employees with affiliation to the attacking country.
·Denial-of-service (DoS) Attacks
DoS attacks prevent legitimate users from accessing a website by flooding it with fake requests and forcing the website to handle these requests. This type of attack can be used to disrupt critical operations and systems and block access to sensitive websites by civilians, military and security personnel, or research bodies.
·Electrical Power Grid
Attacking the power grid allows attackers to disable critical systems, disrupt infrastructure, and potentially result in bodily harm. Attacks on the power grid can also disrupt communications and render services such as text messages and communications unusable.
·Propaganda Attacks
Attempts to control the minds and thoughts of people living in or fighting for a target country. Propaganda can be used to expose embarrassing truths, spread lies to make people lose trust in their country, or side with their enemies.
·Economic Disruption
Most modern economic systems operate using computers. Attackers can target computer networks of economic establishments such as stock markets, payment systems, and banks to steal money or block people from accessing the funds they need.
·Surprise Attacks
These are the cyber equivalent of attacks like Pearl Harbor and 9/11. The point is to carry out a massive attack that the enemy isn’t expecting, enabling the attacker to weaken their defenses. This can be done to prepare the ground for a physical attack in the context of hybrid warfare.
3. Examples of Cyber Warfare Operations
-
Here are some well-publicized examples of cyber warfare in recent times.
·Sony Pictures Hack
An attack on Sony Pictures followed the release of the film “The Interview”, which presented a negative portrayal of Kim Jong Un. The attack is attributed to North Korean government hackers. The FBI found similarities to previous malware attacks by North Koreans, including code, encryption algorithms, and data deletion mechanisms.
·Bronze Soldier
In 2007, Estonia relocated a statue associated with the Soviet Union, the Bronze Soldier, from the center of its capital Tallinn to a military cemetery near the city. Estonia suffered a number of significant cyber attacks in the following months. Estonian government websites, media outlets, and banks were overloaded with traffic in massive denial-of-service (DoS) attacks and consequently were taken offline.
·Fancy Bear
CrowdStrike claims that the Russian organized cybercrime group Fancy Bear targeted Ukrainian rocket forces and artillery between 2014 and 2016. The malware was spread via an infected Android application used by the D-30 Howitzer artillery unit to manage targeting data.
Ukrainian officers made wide use of the app, which contained the X-Agent spyware. This is considered to be a highly successful attack, resulting in the destruction of over 80% of Ukraine’s D-30 Howitzers.
·Stuxnet Virus
Stuxnet was a worm that attacked the Iranian nuclear program. It is among the most sophisticated cyber attacks in history. The malware spread via infected Universal Serial Bus devices and targeted data acquisition and supervisory control systems. According to most reports, the attack seriously damaged Iran’s ability to manufacture nuclear weapons.
4. How to Combat Cyber Warfare
The legal status of this new field is still unclear as there is no international law governing the use of cyber weapons. However, this does not mean that cyber warfare is not addressed by the law.
The Cooperative Cyber Defense Center of Excellence has published a textbook that addresses rare but serious cyber threats. This textbook explains when cyber attacks violate international law and how countries may respond to such violations.
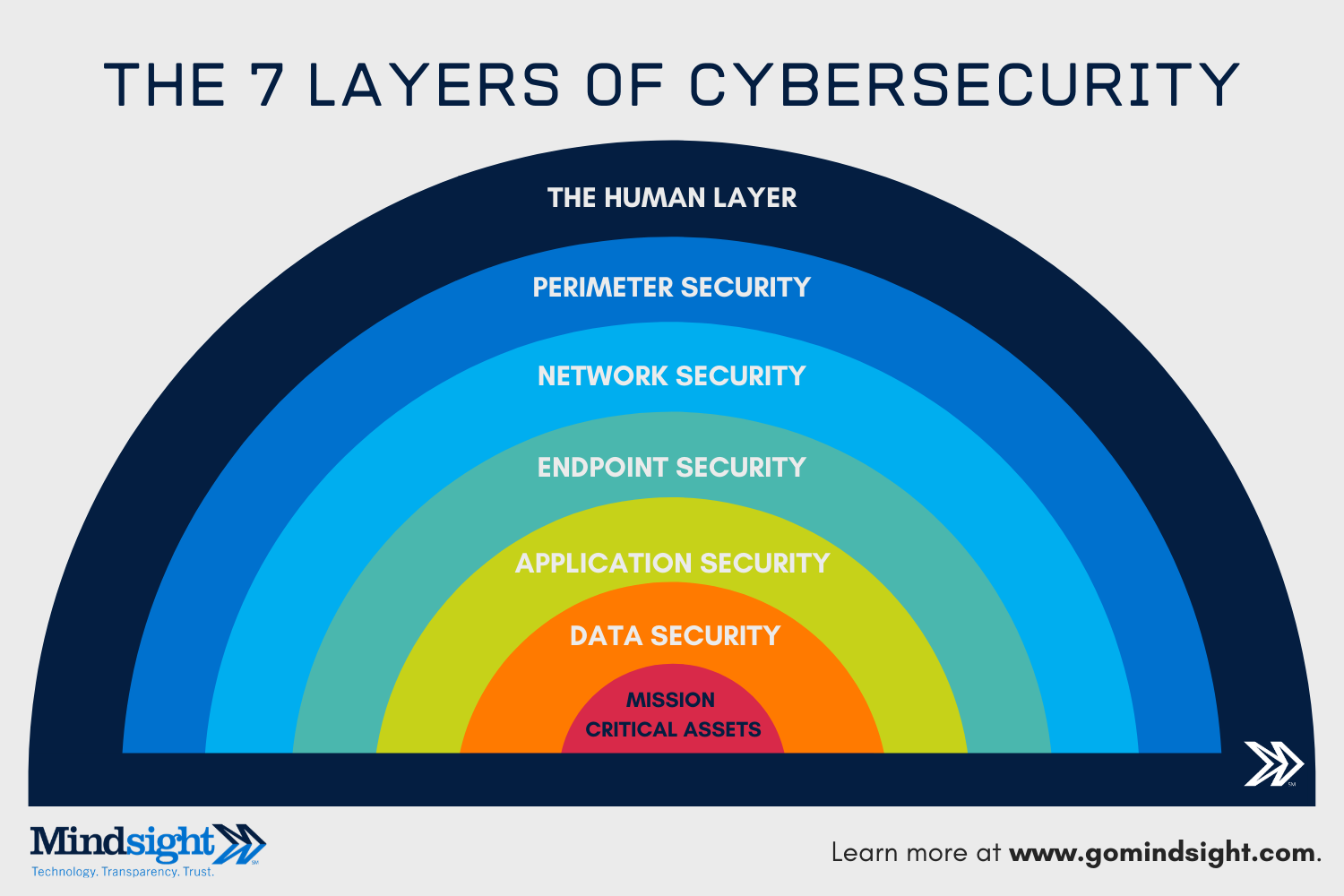
5. The Importance of Layered Defense
Under the pressure of cyber warfare, governments of many countries have issued operational national security policies to protect their information infrastructure. These policies typically use a layered defense approach, which includes:
- Securing the cyber ecosystem
- Raising awareness for cybersecurity
- Promoting open standards for combating cyber threats
- Implementing a national cybersecurity assurance framework
- Working with private organizations to improve their cybersecurity capabilities
Intelligent Transportation Systems: At A Glance
Glossary
- Cybersecurity noun/things that are done to protect a person, organization, or country and their computer information against crime or attacks carried out using the internet:/ There is a need to bolster cybersecurity as government agencies transition to cloud services.
- Policy noun/ a set of ideas or a plan of what to do in particular situations that has been agreed to officially by a group of people, a business organization, a government, or a political party/ It was an unpopular policy and caused a number of conflicts within the party.
- Warfare noun/ the activity of fighting a war, often including the weapons and methods that are used / It was an unpopular policy and caused a number of conflicts within the party.
- Government noun/ the group of people who officially control a country/ The government is spending millions of dollars in its attempt to combat drug abuse
- Security noun/ protection of a person, building, organization, or country against threats such as crime or attacks by foreign countries/ Why would a tenant agree to swap life-time security for a short-term lease?
- Protect verb/ to keep someone or something safe from injury, damage, or loss:/ She’s always chasing cats out of the garden to protect her precious birds.
- Infrastructure noun/ the basic systems and services, such as transport and power supplies, that a country or organization uses in order to work effectively:/ The minister is responsible for the country’s transport infrastructure.
- Defense noun/ the ability to protect against attack or harm, or something used to protect against attack or harm:/ If capitalism were only celebrated for its true merits, as her fiction attempted to do, its defense would be simple.
- Pressure noun/ the force you produce when you press something:/ If you apply pressure to a cut it’s meant to stop the bleeding.
- Issue noun/ a subject or problem that people are thinking and talking about:/ They launched a vehement attack on the government’s handling of environmental issues.
Resources:
- Video: YouTube.com
- Text information: Wikipedia
- Words description: Cambridge University Dictionary
- Pictures in presentation: Google